At the Saudi Arabian Grand Prix, Fernando Alonso scored his 100th Formula 1 podium, then lost it and won again. What kind of mess happened in Jeddah and why is it simply unacceptable at F1 level?

- functions of the foot
- Anatomy of the foot
- joints
- ligaments
- Anatomy of the foot
- Ligaments of the foot
- Horseshoe straps on the heels
- The skeleton of the foot
- joints of the foot
- metatarsal joints
- Subtalar
- The pastern-thigh joint
- The heel bone-foot joint
- wedge joint
- Sudden punishment.
- Where were you during half the race?
- competitor
- Variant 1: on the back
- Variant 2: Reverse horsemanship
- Snail
functions of the foot
The primary functions of the foot include:
There are also secondary functions:
- flexion of the foot backwards;
- flexion of the sole of the foot;
- Diffraction;
- Lateral rotation;
- adduction in the medial plane;
- stretching.
Humans use their feet to move. All movements are carried out with the foot. The toes have a springy function. This means that you can lean on your toes without losing your balance.
Anatomy of the foot
The anatomy of the foot is complex and differentiated.
The foot is composed of four main parts:
- The foot bones. These are further divided into:
- The tarsal bones (the. The tarsal bone consists of seven bones: talus, calcaneus, scaphoid, cuboid and three sphenoid bones. The talus is the largest bone and is responsible for the mobility of the ankle joint.
- Metatarsals. There are five bones in the metatarsal area. Together, these bones resemble a pipe. The ends of the bones extend to the toes. These bones allow the toes to move.
- The phalanges of the fingers. The movement joints are located between them. There are 14 bones in this part. There are three bones in all fingers except the thumbs, and two bones in the thumbs. Through this part, balance is maintained and the ability to perform all kinds of small movements.
- The joints of the foot.
- The muscles.
- The vessels and nerves. They are responsible for the blood supply to the foot.
joints
There are not enough bones to move. Joints are also needed. The largest joint is the ankle joint. It allows the foot to perform various movements. The other joints are not as important, but they ensure the mobility of the joint.
The ankle joint has three bones in its section:
There are also smaller joints:
- subtalar joint;
- The tarsometatarsal joint and the metatarsal joint;
- tarsometatarsal joints (tarso-tarsal joints);
- tarsophalangeal joints;
- Interphalangeal joints.
ligaments

The most important ligament of the foot is the longitudinal ligament or long sole ligament. It begins at the heel bone and extends to the metatarsal bone.
Anatomy of the foot
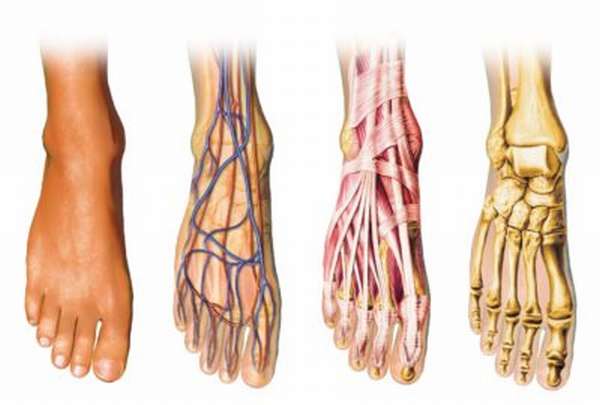
This area of the body is called the distal sphere of the foot - the limb from below. It is a complex joint made up of small bones that form a strong arch and give us support when walking and standing. The anatomy of the foot and its structure become clearer when we know the structure of the foot.
The bottom of the foot that comes into contact with the ground is commonly referred to as the sole of the foot. Its backside is called the hindfoot. It is divided into three parts:
The arched structure and the many joints give the foot great robustness and strength, but also elasticity and flexibility.
Ligaments of the foot
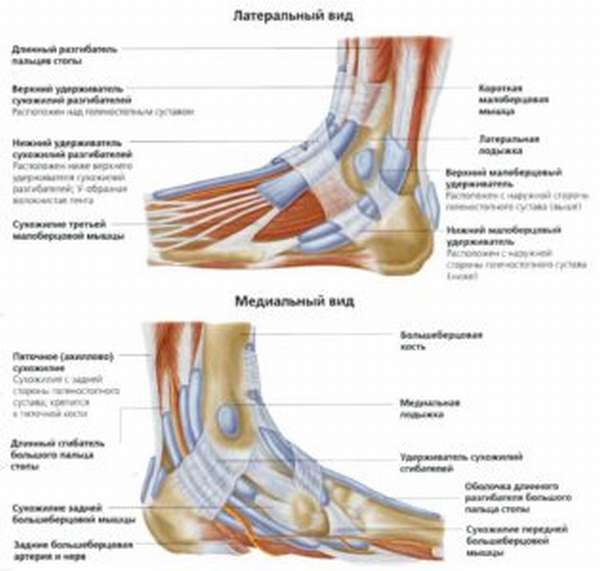
The ligaments of the foot and lower leg hold all the bony structures together, protect the joint and limit its movement. Anatomically, these structures are divided into three units.
The first consists of the fibers that connect the tibia bones together. The interarticular joint is an area with a continuous membrane that extends between the bones of the tibia and the lower extremity. The purpose of the posterior inferior fibula is to prevent the internal movement of the bones. The anterior inferior fibular ligament joins the ankle joint on the outside of the tibia and prevents the ankle joint from rotating outward. The transverse ligament secures the foot against inward movement. These ligaments connect the fibula to the tibia.
The external ligaments are the anterior and posterior peroneal talus and the calf and fibula. They run from the outer region of the fibula in all directions to the tarsal region. They are therefore also referred to as 'delta bands'. They are tasked with strengthening the outer edge of this area.
The next group are the intrinsic ligaments, which run to the side of the joint. These include the tibiofibular ligament, the tibiofemoral ligament and the posterior and anterior humeral ligament. They start on the inside of the ankle. Their job is to prevent the tarsal bones from moving. The strongest bond will not be singled out here - they are all quite strong.
Horseshoe straps on the heels
The formation of corns on the heels is often described as a sign of joint problems. Horseshoe-shaped corns form when pressure is applied to the edges of the heel and are usually associated with deformities of the knee and hip joints and problems with the lumbar spine. Often these deformities are associated with autoimmune processes in the body.

Heels are smooth. How you can help 'both of you' Read more
The skeleton of the foot
In order to understand the structure of the ankle joints, it is necessary to know the anatomy of the bones. Each foot consists of 26 individual bones that are divided into 3 areas.
The tarsus, which consists of 5 short bones located between the tarsus and the proximal phalanges of the fingers.
The phalanges (phalanges) are short bones that form the segments of the fingers (proximal, middle and distal phalanges). All fingers except the first finger consist of 3 phalanges. The big toe only has two phalanges, like the hands.
joints of the foot
metatarsal joints
The metatarsals form a complete group of joints. Let's take a closer look at them.
Subtalar
The heel bone and the talus bone are involved in the formation of this joint. The joint has a cylindrical shape. The joint capsule is only slightly stretched. The surfaces of the bones that make up the joint are covered with smooth hyaline cartilage, to the edge of which the joint capsule attaches. Externally, the joint is reinforced by several ligaments: the intercondylar, lateral, medial and talofemoral ligaments.
The pastern-thigh joint
As the name suggests, this joint is formed by the articular surfaces of the talus, calcaneus, and scaphoid bones. It is located anterior to the talus bone. The talus bone forms the joint head and the other two bones form the joint socket. The joint is spherical but can only move about a sagittal axis. The joint capsule adheres to the edges of the hyaline cartilage that covers the articular surfaces. The joint is reinforced by the following ligaments: talcaneo-ladiform ligament, calcaneo-ladiform plantar ligament.

The joints of the foot
The heel bone-foot joint
It is located between the articular surfaces of the heel bone and calcaneus. The joint is saddle-shaped, but can only be moved around one axis. The sac is taut and anchored to the edges of the articular cartilage. This joint participates in the movements of the two previous joints and increases the amplitude of movement. The ligaments that strengthen it are: the longitudinal ligament of the soleus and the longitudinal ligament of the calcaneus.
Together with the talonavicular joint, this joint is called the transverse tarsal joint. The line of articulation is S-shaped. The two joints are separate from each other, but share a common ligament - the foramen ligamentum.
wedge joint
It is a complex joint that includes the ankle joint, the cuboid joint and the three tarsal wedges. All individual joints are surrounded by a joint capsule that attaches to the edges of the articular cartilage. Mobility is enhanced by the ligaments already mentioned and is low:
Sudden punishment.
But no, that wasn't it. At the very end of the race, the judges suddenly started checking how Alonso's pit stop went. We don't know for sure, but we can assume that it all started with Mercedes - at least George Russell and his team Bridge were actively discussing a possible punishment for the Spaniard. It was probably the Germans who decided to ask the race management why the stewards did not pay attention to Alonso's car being touched by the jack.
Race management asked the stewards to review the moment. The stewards themselves did not do this immediately, as neither the race director nor the FIA's Remote Operations Center (the football equivalent of VAR, so to speak) noticed anything and accordingly did not ask the referees to intervene.
Now, after reviewing the replays, the stewards have admitted: There was contact with the reins. Since this is equivalent to 'working with a car', Alonso has not served his sentence and must receive a new, more severe sentence. Fernando followed in Ocon's footsteps - like the Alpine driver in Bahrain, Alonso also received a 10-second penalty.
Where were you during half the race?
There seemed to be no questions about the penalty itself, but everyone was outraged that the FIA had made the decision so late. The judges ignored Aston Martin's offense for half the race and penalized Alonso after Fernando celebrated his third podium finish. However, had the Spaniard been informed of this during the race, he might have been more than ten seconds ahead of George Russell and would have retained his position. However, the blindness of the race management and the 'withdrawn' judges made the matter pointless.
'You can't give a penalty 35 laps after a pit stop' – Alonso replied to the penalty. – You had enough time to inform me about the punishment. If I had known that, I could have increased my lead to 11 seconds. It wasn't a good spectacle for the fans today.
At the time, there were rumors that the sentence could be overturned because the judges supposedly had no right to punish Alonso after so long. But a careful study of the regulations showed that no, technically there was nothing preventing the stewards from initiating the procedure even after 30 laps.

Alonso thus won the third place trophy.
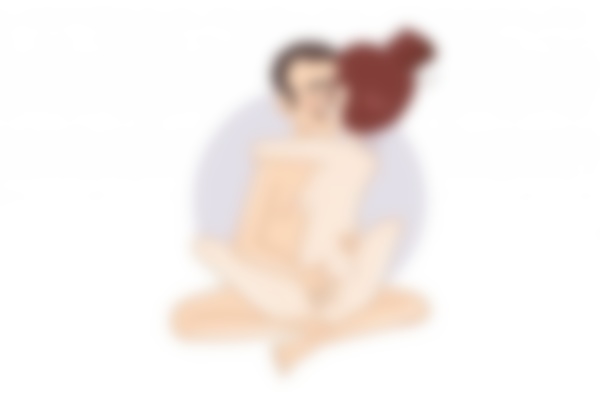
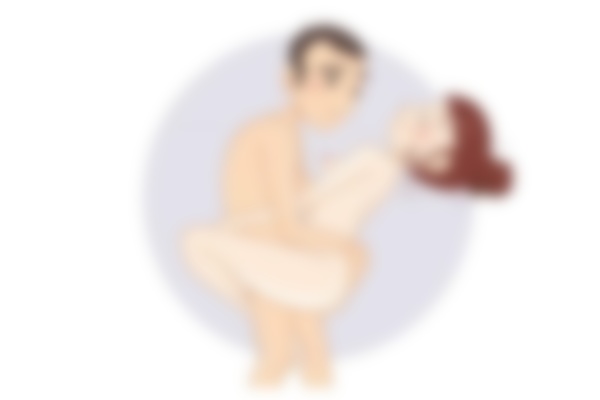
competitor
There's no getting around most men's favorite pose. The technique is very simple: the man lies on his back, the woman on her head. If you want to end the day with passionate sex, the 'cowgirl' position is an excellent choice.
This position requires little preparation and allows the woman to control the process. During the movements the clitoris is stimulated, which is not insignificant for the partner. The beautiful sight and frenetic energy will make sex unforgettable.

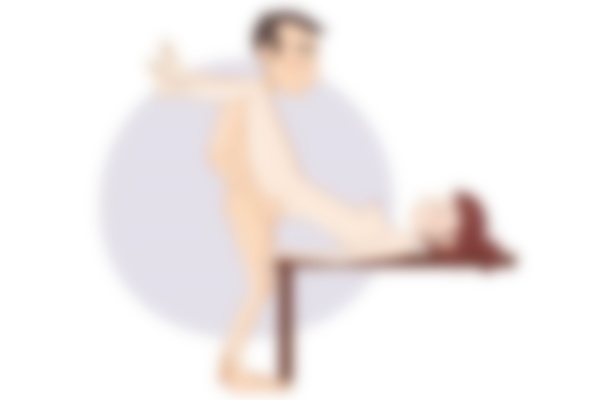
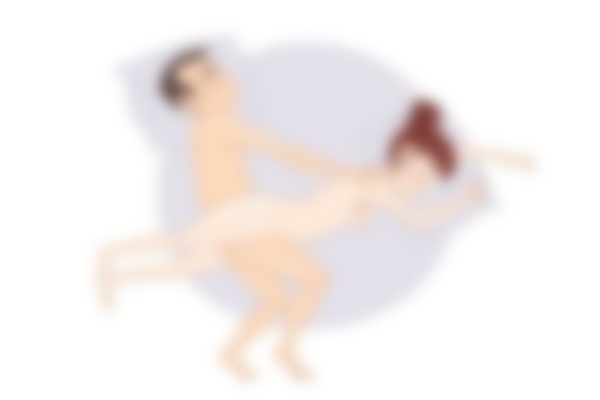
Variant 1: on the back
One of the interesting variations of the classic cowgirl position: the man lies on his back, the woman in the same position on top, for stability you can support her legs on the bed. This position can also be used for anal sex and is beneficial for both the man and the woman.
During the movements, the man can not only caress his partner's breasts, but also stimulate her clitoris, bringing her to a lively orgasm.

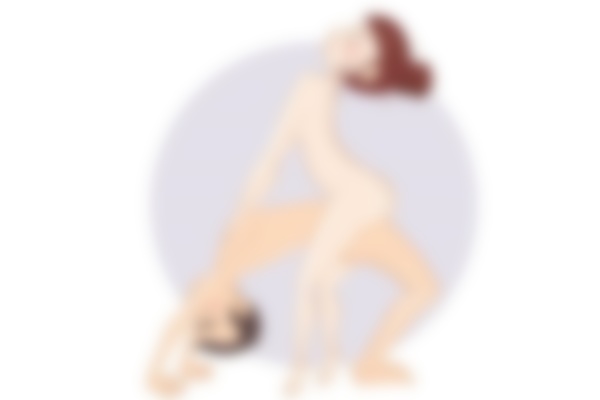
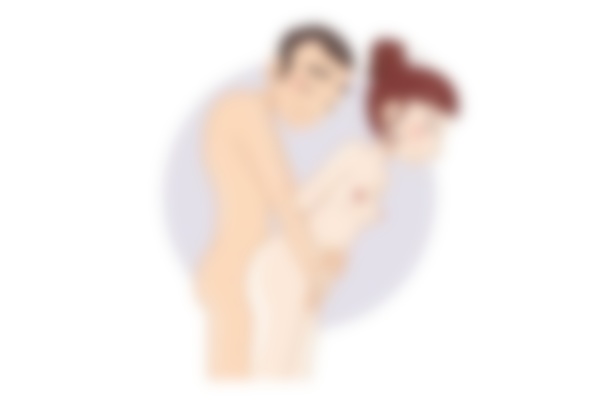
Variant 2: Reverse horsemanship
The woman sits on her partner and turns him around with his back to her. The angle changes, the position changes, this pose becomes more dynamic. The man is easily aroused, and when the woman wears beautiful lingerie, the passion is unsurpassable.

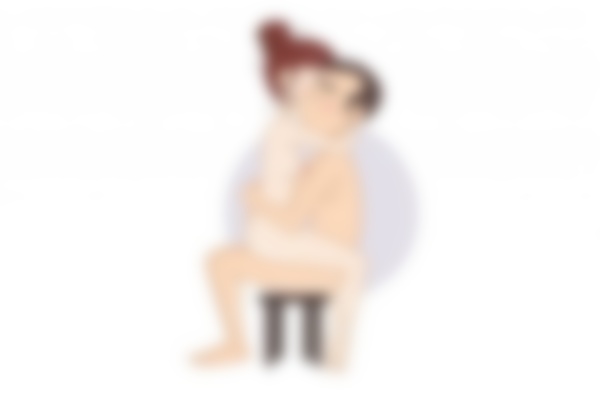
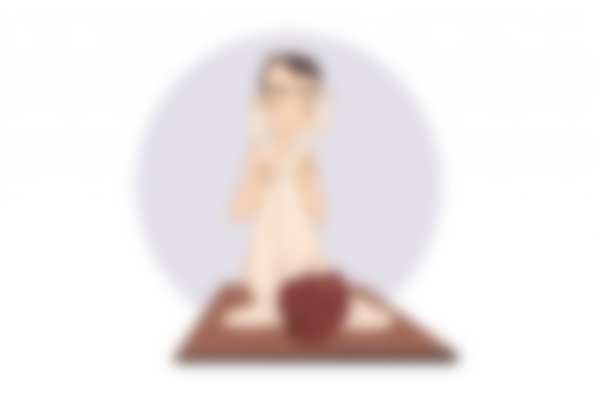
Snail
The technique for the snail pose: The woman lies on her back, her knees drawn up to her chest and thrown over the man's shoulders. This position ensures maximum eye contact and deep penetration. All that remains is to trust the man and receive an unforgettable dose of pleasure.
This is important: The shortest and safest route to female arousal is through the clitoris, which is the trigger for orgasm. Anatomically it corresponds to the male penis, but contains three times as many nerve endings as the tip of the penis. In most women, the clitoris is located some distance from the vagina and the penis does not touch it during intercourse. When the clitoris is near the entrance to the vagina, it is easier for the woman to cum in the missionary or cowgirl position. Other positions require additional clitoral stimulation. Positions in which you can comfortably reach the clitoris with your hand without removing the penis from the vagina are suitable for this. This includes all variants of the kneeling position, variations of the 'man from behind'.
There are 64 postures in the Kama Sutra and each of them will find its followers. The most important thing is that you don't be afraid to talk to your partner about your desires and that you don't be afraid to experiment. The effectiveness of sex largely depends not on the position but on the movements in it, and it is worth learning this together.
Here are some of the most interesting points that everyone should know about:








- Which legs are considered long in women?.
- The intercondylar syndesmosis is the.
- The tarsal bone hurts from above - what to do?.
- Marfan syndrome at a glance.
- What parts of the leg are called.
- Schopar'sche joint.
- Anatomy of the Lisfranc joint.
- Long legs, small body.
