Anal pain can last anywhere from a minute to half an hour.

- flatfoot
- Conservative therapy
- Possible causes
- diagnosis
- Risks associated with flat feet
- diagnosis and treatment
- classification
- diagnosis of the problem
- What causes flat feet?
- How to treat
- How can I get rid of the pain?
- improvise
- Improvisation on TNT
- improvise. tour
- The improvisation. concert
- Improvisation. stories
- Импровизация. Comandy
- Bone marrow infarction on CT scan - what is it?
- Causes of Bone Infarction
- contraindications
- Preparation
flatfoot
In flatfoot, the arch of the foot flattens and deforms. In some cases, it is accompanied by a bumpy, painful, inflamed bunion on the big toe. Despite the invisibility of the disease in the initial stages, flatfoot poses a threat to the entire body, as it increases the load on the knee and hip joints, as well as the spine. It causes annoying pain when walking and exercising, and in severe cases leads to osteochondrosis and spinal deformity.
Flat feet are a common condition in both children and adults. The congenital and static forms of the disease are the most important. The former occurs in 3-5 % neonates, the latter in 10 % adults. Specialists also distinguish between longitudinal, transverse and combined flat feet, each of which has three stages of development.
Treatment of flat feet abroad begins with a comprehensive diagnosis and determination of the cause of the condition. Congenital forms usually do not tend to progress, while acquired forms can quickly deform the foot and cause severe pain. Treatment is selected based on an analysis of the causes and an MRI scan of the foot.
- In the case of longitudinal flatfoot in childhood, conservative methods are the first choice. The flexibility of the ligaments and the training time of the musculoskeletal system allow for complete healing.
- In adults, conservative treatment is no longer as effective and surgery is the only way to correct the defect.
- Bunion and transverse flatfoot are immediate indications for surgery in both children and adults.
Conservative therapy
The comprehensive treatment for flat feet in children in Germany in the first days of life consists of applying a bandage to keep the foot in the correct position. Since the musculoskeletal system in preschool children is not yet formed and flexible, the treatment of flat feet is mainly tonic.
Massage and therapeutic exercises are recommended, wearing special orthoses, walking barefoot on sand and stones is recommended.
In adults, conservative treatment of flatfoot prinimenyutsya only with 1 and 2 degrees. Appointed wear insoles with spinators, padding the foot during movement. Specialists also recommend limiting physical activity and prescribing ointments based on modern anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain. All of these solutions are supportive and do not fix the actual defect - the foot deformity.
Possible causes
- Intrauterine anomalies in the development of the foot
- Traumatic injuries and consequences of improperly healed fractures
- Bone deformities caused by paralysis or paresis of the foot or shin muscles
- Ligament and muscle weakness
- overweight
- period of pregnancy
- Heavy physical exertion
- uncomfortable footwear
- age-related changes in ligaments and muscles
- Weak: vault height 25-35 mm, vault angle 131-140 degrees. No visible deformity. Patients tire with every motor activity. Fluid gait is impaired, swelling and pain sensations in the foot are observed.
- Moderate: The longitudinal arch is 24-17 mm high and the arch angle is 141-155 degrees. The foot is clearly flattened. Gait is impaired and the foot is very painful at rest and with minimal exertion.
- Severe: Longitudinal arch less than 17 mm, arch angle greater than 155 degrees. Constant pain, swelling of the foot and lower leg. Joint and spine diseases (osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis). The ability to work is limited and walking is difficult. It is necessary to wear special orthopedic shoes.
A thickened longitudinal arch in the foot can be determined independently. A footprint should be made on the ground or on paper. The deformity is definitely present when the foot is in full contact with the surface.
The first two stages do not cause much discomfort to the patient and can be successfully treated. The third stage is difficult to treat.
diagnosis
Diagnosis is made with the help of techniques: podometry, planometry i X-ray of the foot..
To calculate the podometric index using the Friedland method: the doctor measures the height of the foot from the end of the arch to the floor and the length of the foot from the heel to the end of the big toe. The height of the foot is multiplied by 100 and divided by the length. The result is the value of the podometric index. His normal value: 29-31. If the index value is 27-29, it may be the beginning of a flat foot. At an index of about 25, the deformity of the foot is evident.
For an accurate diagnosis, plantography and x-rays are used.
Risks associated with flat feet
Flat feet are not only a foot disease, but also a factor in the development of complications:
- joint stiffness, foot contractures;
- Injuries to the joints, bones and muscles of the feet, especially the knees;
- Movement disorders (rheumatism, osteochondrosis, etc.).
- Development of foot pathologies - severe deformities of the toes, articular arches and foot surfaces - a frightening sight that leads to shoes not fitting anymore;
- joint pain, spasticity of the muscles of the lower limbs and feet, arthrosis, diseases of the lower limbs, it is difficult to walk and perform therapeutic exercises;
- In later stages, changes occur in the spine and other parts of the body.


diagnosis and treatment
- The inner corner of the sole or heel part of any material will rub off more, the heel 'slips' inwards;
- The feet widen, a 'ball' develops on the toes, the shape and appearance of the foot change;
- corns appear on the feet;
- Heels and toes almost always sore after exertion and standing work;
- The feet have a completely flattened appearance.
You can determine transverse or longitudinal flat feet at home by making a footprint on the floor. Place your wet feet on a piece of paper and you will see the shape of the foot on the surface.
The larger the area of the footprint, the more pronounced the flatfoot. The longitudinal arch of the foot should not touch the ground.
This method is good for identifying deformities in children from the age of three, since before this period the foot is not formed, and the flattening of the foot is the anatomical norm.
For people who like to wear high heels, the angle of their feet changes when they walk, which affects their appearance. The podiatrist must determine the extent of the foot pathology and develop a diagnostic tactic as well as a treatment for the condition.
Children's feet are flat: This is due to the progressive development of the bones and muscles of the legs and feet in infants. If you stand with your feet on a piece of paper, you can see the arch of the foot in its entirety. It is believed that the foot muscles and ankle ligaments develop by the age of seven. It is too early to treat flat feet at a young age, but symptoms such as foot pain can occur in children.
Early treatment can relieve some of the pain in the feet and legs. It is important to identify comprehensive foot rehabilitation to strengthen the feet and prevent further foot deformities. Physical therapy helps relieve the foot pain and foot exercises should be done to develop the muscles in the legs and feet.
The doctor diagnoses foot diseases visually and using special methods (X-ray, plantography, podometry, etc.).
classification
Depending on the severity of the anatomical changes and clinical symptoms, longitudinal flatfoot is divided into:
- Grade I - is indicated by a slight deviation of the arch of the foot, the height of the arch varies between 25 and 35 mm. (considering that the normal height for an adult is 35-40mm, for a child under 7 years old it is 19-24mm). It is accompanied by fatigue after a long load on the legs, at the end of the day there may be swelling of the distal area and slight pain when palpating;
- Grade II - moderately severe flatfoot is characterized by a reduction in arch height to 17-24 mm. There is marked pain and swelling of the lower limbs, a drop in the arch of the foot, impaired fluent gait, pressure on the feet is painful and causes discomfort;
- Grade III – clearly visible flat feet with an arch height of up to 17 mm. Constant pain in the feet is accompanied by pain in the lower back and knees. Osteochondrosis, knee arthrosis and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system develop. The ability to work and walk is restricted. Wearing your usual shoes becomes impossible.
With timely treatment, the disease can be prevented from developing into a very serious condition. Therefore, if symptoms are detected, the patient should immediately consult a podiatrist.
diagnosis of the problem
Diagnosis of flat feet can be made on the basis of medical history, physical examination, certain tests, podometry, planimetry and X-rays of the feet.
The Friedland podometric calculation method is used to measure the foot, make calculations and determine an index of the course of the disease.
Plantography consists of examining the sole of the foot and printing it on a piece of paper.
The radiographs are taken in lateral view; this position allows the radiologist to calculate the angles and distances between the bones.

Fill out the form and we will contact you
What causes flat feet?
Flat feet can be caused by a number of factors. Most often, it is a congenital defect that is inherited. Other factors that can cause flat feet are being overweight, wearing stiff shoes, or having bad shoes bad posture. A flat foot can also be caused by injuries such as B. fractures or a dislocated ankle.
A flat foot is diagnosed by a doctorYour doctor may prescribe the following investigationssuch as X-raysto check for flat feet. Other tests that may be performed include foot flexion testing and ankle testing joints.
How to treat
Flat feet are common treated with movement and physical therapy. If the problem is severe, there may be a surgery Intervention. The most frequent surgery is an osteotomy in which part of the Bone removed to allow the foot to be properly positioned. Other operationscan be the removal of a tendon or ligament and the use of an endoprosthesis.
A flat foot is a foot defect in which the foot protrudes outwards. This can lead to pain in the feet, Kneel i MoveThey can cause pain in your feet, knees, and back, and problems walking. Flat feet can be divided into three main types.
Transverse flatfoot is a form of flatfoot in which the feet tend to stick out.
Transverse flatfoot is a common orthopedic problem that can lead to serious health consequences. It is a condition that deforms the foot and can lead to pain and reduced mobility.
Transverse flatfoot is caused by an abnormal position of the feet in relation to one another. It can be caused by congenital abnormalities but is more commonly brought on by environmental factors. It can be caused by wearing unsuitable footwear, but also by injuries, illnesses and being overweight. A transverse flat foot is common in people who have problems with their feet spineIt is common in people who have back problems and in people who have trouble walking.
Treating a transverse flatfoot can be very difficult and time consuming, so it's important to have a to see a doctorif you have problems with your feet. Treatment for transverse flatfoot may include the following surgery Treatment may include surgery, but also medication and exercise.
A longitudinal flatfoot — or transverse flatfoot — is a foot defect in which the feet tend to align. It is a problem that can cause pain in the following areas feetcurvature of spine and other health problems. The longitudinal flatfoot can be treated. with the help of orthopedic shoe inserts, exercises and surgical Surgery.
How can I get rid of the pain?
As we already know, rectal and abdominal pain has different causes, so only a doctor can prescribe a treatment. However, if the patient already knows where the pain is coming from, you can try to relieve it yourself. The following methods may be helpful:
Taking stool softeners or eating foods that contain fiber to reduce pain during bowel movements. Diet is also important in the prevention and treatment of anal and pelvic pain. We've explained how rectal and abdominal pain develops and talked about techniques to get rid of the discomfort.
improvise
'Improvisation' is a unique comedy performance with no script or preparation, created before your eyes and in a single moment. Unchanged actors - Arseniy Popov, Dmitry Pozov, Sergey Matvienko and Anton Shastun - play absurd and surprising characters and find themselves in the most unexpected situations! How the actors create unpredictable and beautiful gags can already be seen in several of our projects:
Improvisation on TNT
The first edition of Improvisation aired on TNT on February 5, 2016. In the five years that the show has been on the air, it has garnered a large following. Each new episode is an important event for the creators and fans of the project.
improvise. tour
The improv show often goes on tour. We have already visited more than 250 cities in Russia and neighboring countries. At the big concerts, every spectator can see for themselves that the show is happening here and now, and can even take part themselves.
The improvisation. concert
In 2021, we decided to professionally film some Improvisation concerts and put them on YouTube so that as many people as possible can at least visit our show virtually and feel the atmosphere of the non-televised performances.
Improvisation. stories
A new format whose actors do not appear on TV shows. Stories' is a long form of comedy improvisation. A performance is a complete story that has a beginning and an end. But what the story is about is decided by the audience on the show. The 'Improvisations. Stories' can be viewed on IMPROCOM's YouTube channel.
<iframe src='https://www.yout
Импровизация. Comandy
In the program 'Improv. Teams' on TNT, contestants compete against each other with improvised humor. Each game is a battle consisting of several rounds of improvisation. On the TV stage, the teams compete against presenter Anton Shastun. This is observed by a jury, which assigns points for each successful joke in real time.
In addition to the TV version, the project 'Improv. Teams' also continued on official offline stages across the country. The main offline stage for 'Improv. Teams' is the Hard Stage. Here the teams not only fight for the title of champion, but also for the chance to qualify for the next TV seasons.
On the IMPROCOM website you can find schedules and tickets for the 'Improv. Teams', Improv tickets in Moscow and other cities.
Bone marrow infarction on CT scan - what is it?
Computed tomography is a modern, fast and highly informative diagnostic method. During the procedure, an area of the body is x-rayed. The result is a tomographic image of the structures examined and a 3D model can be created if required. The examination is neither painful nor uncomfortable for the patient. CT scan is not recommended for:
- Pregnant women, as there is an increased risk of fetal abnormalities;
- People weighing more than 150 kg due to the load capacity of the CT table.
With bone marrow necrosis, it is important to determine the focus of the lesion, the boundaries of the pathological process and the time that has elapsed since the onset of the disease. The resulting lesions can be made clearly visible using computed tomography.
The metaphysis — the part between the head and the shaft of the bone — is most commonly damaged as more and more cells become damaged. The size of the affected area can be up to 20 cm.
In the case of necrosis, the internal architecture of the bone is disturbed: the trabecularization has been lost. The area of necrosis may be irregular, linear, round, oval, or any other shape. The images usually show crescent-shaped or wedge-shaped shading.
The necrosis can extend into the area of the joint socket and wedge itself into the articular surface. In this case, the function of the affected joint is impaired.
As a result, sclerosis – a thickening and increase in volume of the compact substance – forms in place of the dead elements. If an old process is found, the images show numerous, irregularly distributed darkening areas. An image is created in the form of sea pebbles or grapes. A narrow streak of translucency appears between the infarction and the bony epiphysis.
Causes of Bone Infarction
For the most effective treatment possible, it is important to establish the etiology of the pathological process. Elimination of the underlying cause prevents new necrosis from developing and existing necrosis from enlarging.
There are three types of bone infarcts:
- aseptic – associated with an imbalance in the blood supply, can be triggered by
- Vascular diseases (atherosclerosis, thrombosis, compression);
- immunological diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, immunosuppressive drugs)
- Diseases of the circulatory system (sickle cell anemia, polycythemia vera, hemophilia);
- Radiotherapy;
- burns or frostbite;
- obesity
- Alcoholism;
- Decompression sickness; etc.
- Tuberculosis;
- Streptococcal or staphylococcal infections;
- Acquired Human Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), etc;
- Lyme disease, etc.
- broken bones;
- Surgical interventions.
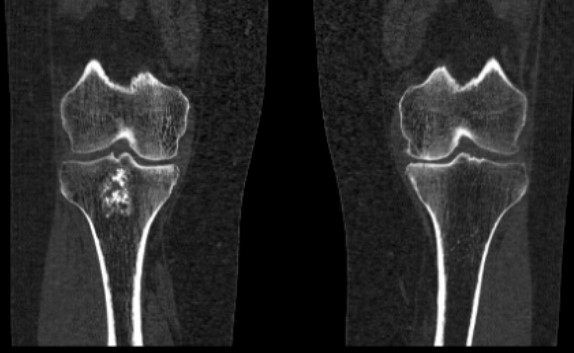
Bone marrow infarction on CT imaging in a patient with deforming osteoarthritis
contraindications
X-rays are an examination with few contraindications. The biggest potential risk is X-ray radiation, which can have a negative effect on the body. However, radiation cannot be completely avoided in everyday life - the devices around us, the earth's magnetic field and cosmic rays from space are all radiative. There are values that are considered conditionally safe for humans. When a doctor takes an X-ray, they know what dose of radiation the patient is receiving, and they make sure it doesn't exceed the safe level. There is no need to worry about the possible harm of an X-ray - several dozen X-rays for adults and three for children can be taken per year. But this happens with old, analogue devices. Modern medical centers are equipped with new digital cameras that emit less radiation. This ensures that the investigation does not cause any damage. Treatment without an accurate diagnosis and understanding of the problem can only worsen the condition.
Particular caution should be exercised in pregnant women and children under 14 years of age. However, for broken bones and other emergencies, X-rays are done at the doctor's discretion. A protective apron is worn to protect the internal organs of the abdomen and chest.
Preparation
X-rays of the feet can be taken without any preparation. It is sufficient to remove shoes and any jewelry at the examination site.
Foot x-rays are usually performed in two projections:
- Stretch – performed in many osteoarthritic conditions and injuries. The foot stands upright on the camera shot. The heel and tarsal bones, the lower part of the tibia and the ankle are clearly visible in this image.
- Laterally - this picture shows not only deformities, fractures and lesions but also longitudinal flatfoot. The patient turns his leg sideways to the camera.
X-ray of the foot in oblique projection - at an angle of 45 0 - is used less often. It is instructive for diagnosing the forefoot, which may not be in the image area of straight or lateral projection.
X-ray examination of the foot in two projections is carried out in a supine or sitting position. The foot is fixed to avoid movement and blurring in the image.
Depending on the suspected diagnosis, the doctor may also order a stress X-ray. In this case, the foot is also X-rayed in 2 projections, but while standing and under load. Stress testing is most powerful in flat feet to assess the nature and degree of the deformity and the dynamics of its progression.
The images are evaluated by a radiologist who prepares a written report describing the anomalies detected and their characteristics (location, size, structure).
You register by selecting the department in your city.
- Longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot.
- The longitudinal arch of the foot is.
- Determining the number of longitudinal arches in the human foot.
- Which ligaments strengthen the transverse arch of the foot?.
- Which doctor treats flat feet?.
- flat feet (valgus foot).
- bones of the foot.
- The largest bone in the skeleton of the human foot.
