Then shower and apply an anti-cellulite product.
- Injuries that result in a thigh muscle strain
- Symptoms of a thigh muscle strain
- diffraction
- glute bridge
- Stretching the quadriceps muscle in the thigh
- stretching of the spine
- reasons
- Treatment
- Thigh
- What is the inflammation of the obturator nerve?
- Stretching the hamstrings while lying down
- Stretching of thighs, shins, shoulders and back while lying down
- Basic principles of thigh correction
- The most effective exercises
- complications
- Conclusion
Injuries that result in a thigh muscle strain
It is not uncommon for athletes to have hip dislocations treated by trauma surgeons. This injury is most common when performing lunges, lunges, and squats.
If after an exercise there is a sharp pain that is so severe that it is impossible to repeat the exercise, it is a sprain. But do not panic or worry, if all therapeutic manipulations are carried out at once, you can quickly return to an active lifestyle.Let's turn to anatomy and see the cause of the pain, the situation is as follows. There are three muscle groups in the hip area:
The adductor muscle guides the hip, the other two are responsible for extension and flexion of the leg. Because the quadriceps and hindfoot muscles run through the hip and knee joints, they are more prone to injury than others. In addition, these muscles are constantly exposed to high loads, especially during vigorous physical movements, fast running or walking, high or long jumps and sports (volleyball, basketball, football). The back and thigh muscles can be strained or stretched to varying degrees, with 3 levels:
- Severe pain but no bruising;
- There is severe pain and bruising.
- The muscle is completely torn and there are many large bruises.
In the latter case, it can take up to several months to regain the same physical shape.
He specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory and allergy diseases and has knowledge in the areas of external respiratory function testing, allergen testing, autohaematology and specific and non-specific immunotherapy.
Symptoms of a thigh muscle strain
To diagnose a biceps brachii or iliolumbarus strain, several symptoms should be noted: First, there is a 'clicking' sensation; secondly, there is severe pain and it is painful to touch the injury; third, there is visible bruising, and sometimes a large bruise.
After the injury, it is difficult to keep moving, let alone play sports. There is a greater risk of the same injury causing permanent damage in the future, which is why it's extra important to follow all of your doctor's and trainer's recommendations. Further diagnosis is carried out by a surgeon or trauma surgeon.
The doctor must find out under what circumstances and with which movement the injury occurred, what kind of tenderness the patient has and how big the bruises are. The doctor will ask the patient to flex and straighten the leg at the knee and hip joints, and then make a diagnosis. It is necessary to take into account these symptoms of a hip muscle strain and, in addition, take an X-ray.
diffraction
Stand up straight and place your feet hip-width apart. Put your hands behind your head and keep your elbows wide apart. Slowly bend your body forward while actively contracting your cortical muscles. Don't arch your lower back or arch your back. Feel your hamstrings stretch. Then gently return to the starting position. Perform 8-10 repetitions.
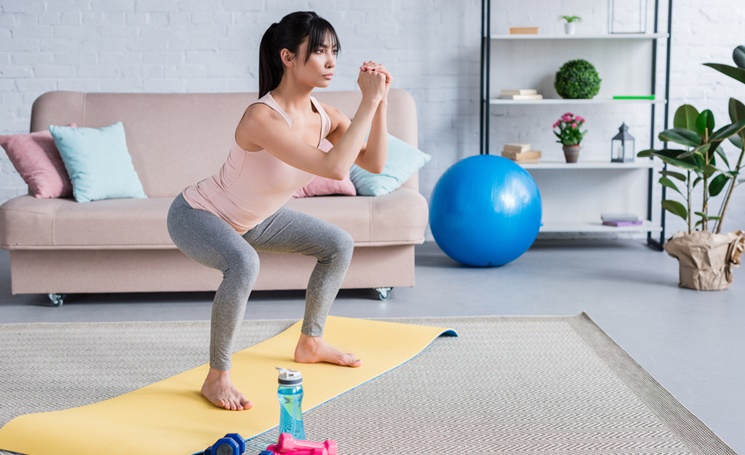

Stand up straight, feet hip-width apart, bend your knees slightly, and angle your toes slightly outward. Engage the cortex and abdominal muscles by bringing your chest forward and then slowly pulling your hips back while bending your knees. Lower yourself until your hips are almost parallel to the floor. Then gently return to the starting position. Perform 8-10 repetitions.
glute bridge
Lie on your back on the floor, bend your knees, place your feet on the floor and stretch your arms out along your body. Slowly tighten your glutes and push your feet off the floor toward the ceiling. Try to straighten your torso and hips in a diagonal line from your shoulders to your knees. Don't tense your neck, tense the backs of your thighs. Slowly lower your buttocks back to the floor. Perform 8-10 reps.
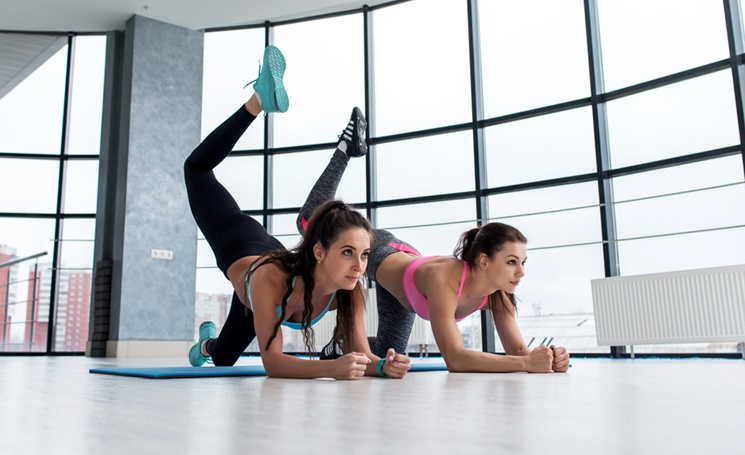

Bend your knees. Bend your body forward by placing your hands under your shoulders and your knees under your hips. While engaging your abs, glutes, and legs, raise your right leg off the floor by first extending your foot toward the ceiling, then extend your leg back and your foot touches the floor. Then bend the knee and return to the starting position. Perform 8-10 repetitions on each side.
Stretching the quadriceps muscle in the thigh
Exercise #1.: Standing quadriceps stretch on one leg
A classic exercise that you can do anywhere. Even on your lunch break at work. Stand up straight, bend your leg at the knee, and grasp your shin with your hand. Keep your knees together. If you find it difficult to keep your balance, use your hand to support yourself on a chair in front of you or on a wall. Pull the heel as close to your buttocks as possible. After 30-50 seconds, repeat the exercise with the other leg.
The exercise is great for stretching the front of the thigh, improving mobility and relieving muscle tension. It has a decompressing effect on the knee joint.
Exercise 2.One step quadriceps stretch.
Stand up straight, bend backwards and place your knee on the floor. If you find it difficult to balance, you can lean on a chair with your free hand. Grab your left foot with your left hand and try to pull it toward your buttocks. After 20-30 seconds, repeat the exercise with the other foot.
stretching of the spine
Exercise #1. Pashchimottanasana. Stretches the muscles of the back and legs.
Sit on a mat, straighten your legs and bring them together with toes pointing up. Tilt your pelvis back slightly and let go of your seat bones. As you inhale, grab your toes with your hands and as your back tightens, bend your knees. Draw the shoulders and shoulder blades back and the ribs forward and up. Then, as you exhale, relax your back and alternately lower your abdomen, ribs, chest, and head to your feet. Keep your hands on your feet or place them on the floor. Relax your toes and point them slightly forward, relaxing your shoulders and neck. Close your eyes and stay in this position for 30-60 seconds, breathing deeply and evenly. Watch how you feel.
Try to reach your feet not with your head and chest, but with your lower abdomen. First the head and upper body are pulled forward, then the stomach towards the hips. A special belt can be used to start with.
Exercise 2. Downward Head Dog
There is an opinion that this asana is not a stretching exercise. In fact, it's a full-body stretch, from your lower legs to your thighs to your back.
exercise 3. Upward Facing Dog or Cobra (urdhva mukkha shvanasana) is the easiest and most accessible iliac muscle stretching exercise.
Lie on your stomach and place your palms on the floor, shoulder-width apart. Gently lift your upper body backwards with your lower body resting flat on a hard surface.
It is important not to lift the pelvis and legs off the floor and to make sure that there are no painful sensations in the lumbar spine.
reasons
The semimembranosus muscle is attached to the inside of the bone at the ischium and the top of the tibia. You straighten your hips and bend your knees. These muscles are injured when the hip is maximally flexed and the knee is extended, a position in which these two muscles are maximally stretched. For example, this is the position of the leg immediately after the ball is thrown in soccer. When you hurdle or split, the hamstrings in your front leg are at risk.
Overstretching contributes to trigger points in the hemispheres, as does inactivity. Their length decreases with sitting all day and evening at work, in the car and at home. Constant pressure on the lower legs from the edge of the seat interrupts blood circulation and also contributes to trigger points.
A stiffened tendon is often the first cause of chronic lower back pain. They destabilize the pelvis, flatten the natural curve of the lower back, and disrupt the mechanics of the back and gluteal muscles. Postural changes that B. with
The head is pushed forward and the upper back and neck are put under extra strain. Stiffness in the neck tendons therefore has a knock-on effect, causing pain in more distant parts of the body, including the jaw, face, and head. In other words, your tendons may even be the source of your only ailment—headaches.
Treatment
Locate the seat of the semitendinosus at the back of your inner thigh. Examine this entire area with a tennis ball placed under the thigh on the seat of a wooden chair, as you did with the biceps femoris (see Figure 9.46). Move your foot on the ball from side to side across the full width of the thigh. Most trigger points are found in the middle and lower thighs, although they can often be found under the ischial bone as well. In Fig. 9.4 7, each black dot in the lower half of both muscles marks the location of possible multiple trigger points in the semitendinosus muscle, which is hidden under the semitendinosus. You may not be aware of the existence of trigger points in your hamstrings unless you carefully look for them. The most important thing about all hamstrings is that they cannot fully stretch unless you eliminate the trigger points in them that severely impede the stretching of the muscle fibers. Routine stretching before a workout can make you feel like you're doing the right thing for your muscles, but when trigger points are present, there's a risk of them becoming damaged.
Based on Trigger Points by Claire Davies and Becoming a Supple Leopard by Kelly Starrett
For a consultation and a training appointment:
Thigh
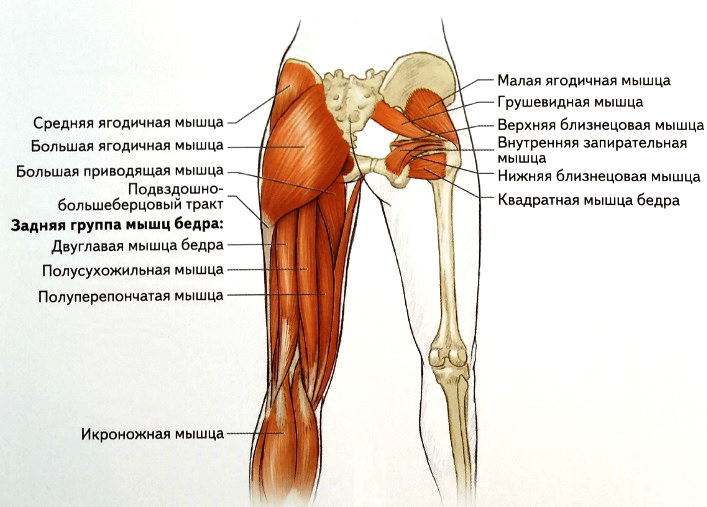
The muscles of the thigh are what are known as the free limb muscles. They are also divided into three groups of movements. The classification is done in this way:
- flexor. This includes the tissues at the front of the limbs - the biceps, the quadriceps. In contrast, they straighten the shin.
- extensors. This group includes the elements of the hamstrings - biceps, quadriceps and extensors. They also flex the shin.
- medial. The function is adduction with some outward guidance. This group includes the thin adductors, the flexors, and the 3 adductors.
The major muscular components of the hip joint itself are the hip and gluteus medius muscles, but the role of the other players in this area should not be underestimated. Muscle weakness can be an indirect cause of hip joint laxity.
Strengthening the muscular corset in the hip area is one of the main recommendations of orthopedists. Strong muscles not only make the figure more attractive, but also prevent ligament injuries and promote blood circulation in the hips, shins and feet. In addition, the joint itself is well supplied with blood, which means that degenerative diseases such as arthrosis can be avoided.
We would be very grateful if you would rate this article and share it on social media.
What is the inflammation of the obturator nerve?
Near the femoral nerve is another nerve - the obturator nerve. If you develop inflammation of the nerve there, you will experience the following symptoms
- You can't put your foot on your leg.
- You have difficulty rotating your leg outward.
- Decreased sensitivity of the skin on the inner thigh.
You should be evaluated by a neurologist to properly understand the symptoms of the condition. See your doctor at Medicina24 International Medical Center as soon as you notice any of the neurological disorders described on this page. Call any time day or night: +7 (495) 120-19-58.
This material was created by Nurutdinova Elsa Niazovna, Neurologist at Medicina24 International Medical Centre.
Stretching the hamstrings while lying down
Lie on the ground by the door. Lift your right leg and place it against the wall. Keep right leg straight at knee, left leg free on floor. Place your palms on the floor with your palms on either side of your buttocks. Without bending your right leg, use your hands to pull your body up towards the door until you feel a pain in your leg from the stretch. working muscles
Mainly: gluteus right, semitendinosus and semitimembranosus right, biceps right thigh muscle, biceps right calf muscle.
To a lesser extent: right fibula, hamstring and plantar muscles, right long toe flexor, right posterior tibialis, left sartorius, left right quadriceps.
In order to stretch the muscles as much as possible, you must not bend your knees and do not raise your pelvis. Your spine should maintain its natural curve. The closer your buttocks are to the door frame, the greater the stretch. Once you've got your pelvis as close to the door frame as possible, you can increase the stretch by bending your right leg toward your head at the hip joint.
Stretching of thighs, shins, shoulders and back while lying down
Using a towel allows you to engage more muscle groups in the exercise.
Lie on the ground by the door. Lift your right leg and place it against the wall. Keep your right leg straight at the knee, your left leg relaxed on the floor. Take a towel and put it over your foot. Without bending your right leg at the knee and holding the ends of the towel, pull your body toward the door with your hands until you feel pain in your leg from the stretch. Hold the ends of the towel with your hands and pull your foot towards your head.
To a greater extent: gluteus right, semitendinosus and semimembranosus right, hamstring right, erector spinae, quadriceps extensors, calf muscle right, fibula muscle, hamstrings and plantar muscles, toe longus right, tibialis right posterior.
To a lesser extent: left sartorius, left rectus femoris, lower trapezius, posterior deltoid, sphincter major, sphincter lesser, soleus, triceps.
Basic principles of thigh correction
The following principles will help you tone the outer and inner thighs more effectively:
- A holistic approach – a combination of exercise, nutrition and cosmetics.
- A well thought out diet. To get rid of excess weight, you should eliminate sweets, pastries, smoked and fried foods from your daily menu and eat enough protein, fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Drink 1.5 liters of pure water per day to accelerate fat loss and eliminate toxins from the body.
- Exercise to lose weight, taking into account the affected area.
- Anti-cellulite treatments (wraps) and self-massage with warming agents are useful several times a week. You can do this yourself or buy it at the pharmacy.
The most effective exercises
To reduce the volume of the thighs, it is necessary to perform special strength complexes.
- Sumo Squat:
- Straighten your back and spread your legs wider than your pelvis, your arms with the dumbbells along your body;
- Slowly squat down until your knees are at a 90-degree angle;
- Stand up slowly and straighten your legs.
Make sure your back stays straight throughout the exercise. Do this exercise 15 times.
- Side lunges help reduce volume in the thighs and glutes:
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, hands at waist;
- Step sideways and shift your body weight onto your right foot. Bend the knee in a lunge;
- The work must involve the lower body.
Perform two sets of 10-20 exercises for each hamstring muscle group.
Start with small weights and then gradually increase:
- Stand up straight and slightly bend your legs at the knee joints;
- Slowly squat down to mid-shin and back without touching foot.
Straightening your legs works your hamstrings and tightens your glutes. Weights can also be used.
- Stand up straight and hold your arms;
- Extend your leg to the side at maximum height;
- Keep your back straight and your body in a straight line in space.
Perform at least 10 repetitions for each hip.
- Static exercise 'stool':
- Stand with your back to a wall;
- Slowly squat down, trying to drop into a chair;
- At right angles to the hip and knee joints;
- shoulders down;
- Remain in this position for up to two minutes.
complications
After injuries and operations, the consequences of ligament tears in the knee joint cannot be ruled out.
- osteoarthritis and arthritis;
- limited mobility of the knee - contractures;
- recurrent pain;
- Rejection of the transplanted implant.
Important! In order to rule out a contracture after the operation, the knee is flexed and held in this position for some time. Then physical exercises are started to increase the range of motion. Movement of the kneecap prevents scarring of the ligament after a tear.
Conclusion
In order to return to normal life, one should not neglect the pathology, but immediately go to a trauma center and follow all the doctor's recommendations before and after the operation for six months, and in case of recurrence for more than 7-12 months. A balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle increase the effect of rehabilitation.




- lower leg flexion.
- Lift your heels off the floor during the squat.
- On half-bent legs.
- Anterior tilting of the pelvis.
- muscle work while running.
- Exercises for the triceps tibialis muscle.
- Square soleus muscle.
- muscles in the legs.

